Warts are skin growths in the form of nodules or papillae. This is the most common skin condition, affecting more than 90% of the world's population. Warts can appear in anyone, at any age, on absolutely any part of the skin, from the face to the feet. The disease is often contagious, it all depends on the person's immune system.

What causes warts?
It is commonly believed that touching a frog causes warts to develop. It's a deception. The causative agent of the disease that leads to the formation of warts is infection with human papilloma viruses. According to statistics, this infection causes about 20% of all cancers.
The risk of an HPV infection increases significantly:
- when using personal hygiene items and items of other people's general use;
- in public places (swimming pool, bathhouse, etc. ), especially if you walk there barefoot;
- in case of skin damage;
- with increased sweating of the hands and feet;
- upon contact with an infected person (handshake, sexual contact, etc. );
- when walking in tight, uncomfortable shoes that cause friction on the skin of the feet;
- when using non-sterile instruments (in a beauty salon, etc. ).
Are warts always dangerous?
Most warts are completely harmless and can theoretically disappear within a few weeks or a month at most. In this case, patients are more likely to fear a serious cosmetic defect that causes psychological discomfort and interferes with leading a full-fledged lifestyle.
Warts are often painless unless they are on the soles of the feet or another part of the body that is subject to shock or constant contact. However, there are cases of itching and discomfort in the affected area.
How to recognize warts: symptoms and signs
An inexperienced person might confuse warts with other skin growths, such as moles, calluses, or melanomas.
The main differences between warts and moles:
- Birthmarks have a dark or black tint, while warts have a light color;
- Warts grow closely with the skin, moles are separate structures, as if glued to the body;
- Moles feel soft and smooth, warts are hard, hard and rough.
It is also easy to distinguish a wart from a callus. When pressing on the growth, painful sensations occur, and when it peels off, traces of bleeding are visible underneath. There is new, tender skin under the cornea.
You can distinguish a wart from a melanoma by its color and shape. This dangerous disease is characterized by heterogeneous red and black tones, overgrowth and an uneven contour.
It is not difficult for a dermatologist to make the correct diagnosis based on a visual examination. But a good professional will not be satisfied with a simple inspection. He will definitely use a special magnifying device - a dermatoscope. If a pathogenic process is suspected, scraping of the surface layer is necessary.
In the case of anogenital warts (in the area of the anus and on the genitals), consultation with a gynecologist or proctologist is necessary.
What is the structure of benign neoplasms?
The outgrowths consist of cells that have partially retained their original functions and can grow slowly. Their structure is similar to the tissues from which they were created. They can exert pressure on surrounding tissue, but do not penetrate it because they have a capsule in their structure. They respond well to hardware and surgical treatments and usually do not cause relapses.
There are always congenital formations on the skin – moles or warts, but also acquired ones. The latter arise on the surface or in the subcutaneous tissue as a result of metabolic disorders, reduced immunity or under the influence of a virus.
Common (simple, vulgar) warts
Common warts are dense, dry growths characterized by an uneven and rough surface, variable size and rounded shape. They look like a hard, keratinized blister up to 1 cm in diameter that protrudes significantly above the surface of the skin.
The surface of common warts is often covered with grooves and protrusions, which is why the new growth vaguely resembles a cauliflower or raspberry with black dots inside.
This is the most common type of wart and accounts for up to 70% of all skin neoplasms. Simple warts can appear on the skin at any age, but children and adolescents are most commonly affected. This is because they have weaker immunity than adults.
Common warts usually appear on the hands (fingers and backs of the hands), knees and elbows, sometimes on the face or feet and extremely rarely on the oral mucosa.
Scattered small growths may form next to the large "mother" wart. Young neoplasms usually remain flesh-colored and over time acquire a dirty gray or gray-brown tint, less often yellow or pink. This is due to the uneven porous surface on whichdirt accumulates.
As a rule, vulgar warts do not cause concern: they do not cause unpleasant symptoms, do not hurt and do not itch. However, they can cause pain if they are in impact-prone areas or come into contact with clothing. The growths may heal on their own over time, especially if they appear in childhood.
Why do benign formations appear on the skin?
Cosmetologists and dermatologists do not know the exact mechanism of their formation. The most common cause is:
- injuries;
- viruses;
- systemic diseases of the body, for example xanthomas, arise from an excess of fat in the blood;
- long-term skin diseases;
- exposure to aggressive substances;
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- X-rays;
- Heredity (for example, seborrheic dermatosis).
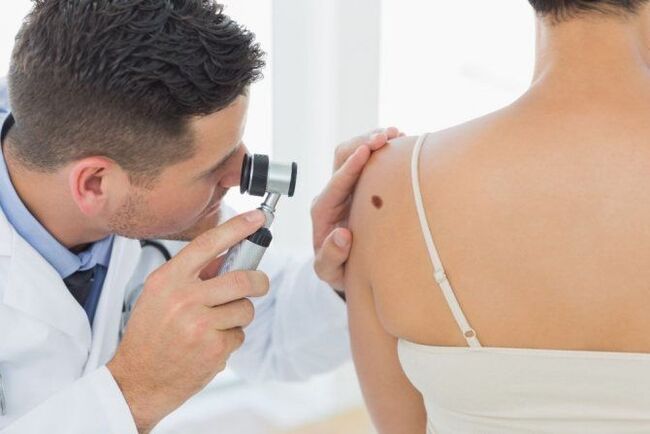
Most skin lesions are benign
plantar warts
Plantar warts are a type of common wart. The manifestation of the disease is most often observed in children and those aged 20-30. Plantar warts occur in 30% of all skin warts.
Warts on the soles of the feet appear as hard, round lumps with papillae in the center. Characteristic black dots are visible inside the wart - many small thrombosed capillaries. There is a small roll of keratinized skin around the edges. The visible part, protruding only 1-2 mm above the surface of the skin, can reach 2 cm in diameter and is only a quarter of the total size of the plantar wart, which forms mainly in the deep epithelial layers (skin).
Externally, the spine resembles a callus. A plantar wart can be differentiated (differentiated) from a callus by the visible disruption of the skin pattern corresponding to the wart.
This type of neoplasm usually affects the feet (soles, sides and toes) and, less commonly, the palms of the hands. They appear on the skin as small whitish, dot-shaped skin lesions that are sometimes itchy. Over time, their surface becomes rougher and changes color - from yellow to dark brown.
Plantar warts themselves do not pose a threat to health, but they cause significant discomfort when walking, cause pain, which often increases and can even bleed. This is due to the location of the tumor and the peculiarities of its growth. As the spine grows inward, the weight of the body presses on the pain receptors when walking.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from several days to several years. The infection enters the body and waits for the activation of a favorable environment. In 50% of cases, plantar warts resolve without treatment. However, this process takes between 8 months and a year and a half.
Without treatment, plantar warts enlarge and multiply, even forming large tumor clusters. This can even lead to a temporary loss of ability to work due to unbearable pain that prevents walking.
Based on the characteristics of the lesion and its location, plantar warts are divided into three types:
- simply;
- periungual;
- Mosaic.
Do benign formations hide the danger?
Benign neoplasms are unpredictable structures that can manifest at any time or not at all. The process of their transformation into malignant ones has not been fully studied. There is no clear answer to the question of what exactly triggers this process. Mechanical trauma, excessive ultraviolet radiation, metabolic disorders and other factors are believed to contribute to degeneration. If you have a benign skin lesion, you should not experiment one way or another and rely on chance. In addition, today the removal does not cause any difficulties.
Periungual plantar warts
Periungual warts are small, rough formations with cracks on the surface that are found on a person's hands and feet, near the nail plate or deep below it. Externally, they resemble heads of cauliflower.
They can be flat, pointed or hemispherical. Periungual warts are usually gray, but can also be flesh-colored. They are not too dense like simple plantar plants, but have a fairly deep root.
Children and young people are particularly affected by this disease. The main factor in contracting the infection is skin microtrauma around the nail. Particularly at risk are those who bite their nails and pet stray animals, as well as people who carelessly remove cuticles, use non-disinfected tools and work in water without gloves.
This type of neoplasm does not pose a threat to human health, it is essentially just a cosmetic defect. Periungual plantar warts do not cause discomfort or pain when pressed. However, a wart under the nail is not so harmless - over time, the new formation leads to depletion of the nail plate and its further destruction.
In addition, various bacteria and viruses penetrate through cracks in the surface of the growths, which are easily formed as a result of frequent manual work, and lead to re-infection. Additionally, as warts grow, the cracks can cause pain. The cuticle is often lost and there is a tendency to inflammation (paronychia).
Removal of the tumor is necessary to stop the growth of growths that easily spread to healthy fingers. The location of the wart under the nail plate makes treatment and removal very difficult. If it occurs during childhood or adolescence, it may go away on its own.
Where do warts come from? They are contagious!
Like herpes, warts are the result of a virus. More than a hundred types of viruses are responsible for causing warts, most of which are HPV. Since there are oncogenic types of HPV, some formations can be particularly dangerous in terms of cancer, such as those that develop around the genitals.
No matter what type of warts they are or where they are located, never pick, rub, or scratch them as they can spread millions of viruses to other areas of the skin where new growths can form!
It is very easy to contract wart viruses. For example, infected human epithelial cells end up in swimming pool water. They swim in the water and easily find their prey. The wart virus can also spread through direct physical contact, such as shaking hands. Penetration of viruses into the body is facilitated by tiny lesions on the skin.
In children, finger sucking or chewing often causes warts under their fingernails, which can be painful and difficult to treat. Children can easily become infected with viruses while playing. This is why one in four children has viral warts on their hands or feet.
Whether we become infected with the virus or not depends on how strong our immune system is. A strong immune system suppresses the infection that causes warts.
Mosaic sole warts
Mosaic warts are a special form of neoplasm. These are plaques, so-called clusters, which are formed by the fusion of many small plantar warts pressed tightly together. The arrangement of the panels resembles a mosaic (hence their name).
This formation is usually observed in a small and localized area. It can reach a diameter of approx. 6-7 cm. In the early stages of development, mosaic warts look like small black punctures. As they develop, they look like a white, yellowish, or light brown cauliflower with dark spots in the center. These spots are caused by thrombosis of the blood vessels.
This type of wart is quite rare. They usually affect the hands or soles of the feet and are particularly common under the toes. Unlike simple plantar warts, mosaic warts cause little or no pain when walking because they are flatter and more superficial.
Mosaic warts are highly contagious. Due to the diversity of foci of viral infection, they are difficult to treat. The success of treatment is made easier by starting it on time. Mosaic growths usually tend to recur even after surgical removal.
Benign and malignant neoplasms on the skin: what are the differences?
Benign pathologies do not pose a threat to human life. If they reach a large size, they can interfere with the proper functioning of various body systems. Malignant ones, on the other hand, grow quickly and aggressively, invade surrounding tissue and form metastases over time. Some damage vital organs and cause death.
Sometimes benign skin tumors change due to external or hereditary causes. They acquire the ability to degenerate into malignant pathologies. Such conditions are referred to as borderline or precancerous. They pose a great threat to health and life, although they are not always accompanied by pronounced symptoms.
Flat (juvenile) warts
Flat warts are a fairly common and least problematic type of tumor. They present as small lens-shaped lesions (several mm in diameter) or as smooth papular lesions. They can either grow singly, which is quite rare, or in large numbers close to each other.
There are several stages of the disease:
- mild – one or more painless warts;
- medium – 10 to 100 painless growths;
- severe – more than 100 neoplasms.
When localized in places where there is excessive pressure (friction from clothing, shoes, etc. ), they cause pain.
Flat warts are easy to recognize and have a white, brown, yellowish or pink hue that resembles the color of flesh. They are about the size of a pinhead and are smoother and flatter compared to other types of warts. In fact, at the point where a flat wart develops, the skin rises slightly (to a height of about 5 mm) and forms a kind of raised circular area.
The growths typically appear on the face, knees, elbows, back, legs, and arms (especially the fingers). People of all ages fall victim to this disease. But most often children and adolescents are affected by it (20% of schoolchildren have it), hence the second name for warts - juvenile.
In a narrow group of school children, 80% show resistance (resistance) to the virus. In adults, irritation and inflammation after shaving contribute to the spread of tumors.
The incubation period of an infection can last up to 8 months. Most of the time the disease is simply a cosmetic defect. Juvenile warts are painless unless caused by mechanical pressure or injury and can sometimes cause itching, but are extremely contagious.
There is practically no transmission of the virus via shared objects; the main route of infection is skin contact. Flat warts multiply so easily that it is enough to touch a healthy part of the body to provoke a new formation.
The peculiarity of this type of wart is that in most cases no treatment is required: they can disappear as suddenly as they appeared, especially in children. In adults, the disease requires treatment and the virus is very resistant to drug treatment.
Transmission of warts through direct contact
Minor trauma or maceration leads to epithelial barrier dysfunction and subsequent loss of skin integrity, paving the way for viral infections and wart formation. The incubation period is 3 weeks to 8 months after exposure. In most cases, spontaneous regression is observed.
Laser removal of warts
Nowadays, laser surgery is one of the best ways to get rid of warts. This is a painless and safe procedure that can be used in areas of greatest sensitivity. Laser removal of tumors is very effective: the likelihood of relapse is minimal. This is significantly influenced by the severity of the disease.
Warts are removed by cauterizing the affected area in layers, allowing the doctor to control the depth of the effect. At the same time, the laser beam cauterizes the blood vessels, preventing bleeding at the site of impact.
Three methods of laser coagulation are common:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) laser. Procedures with this laser are more painful. Although the CO2 laser seals the blood vessels, it also kills the wart tissue. There is a possibility of damage to healthy tissue. Wound healing usually takes longer and scarring is possible. The efficiency is around 70%.
- Erbium laser. It is characterized by a shorter wavelength. The likelihood of scarring after healing is significantly reduced.
- Pulsed dye laser. This laser more effectively seals the blood vessels that supply the wart. Unlike a CO2 laser, it does not damage much healthy tissue. It is also the only type of laser approved for use on children. The effectiveness of this treatment method is around 95%.
| Advantages | defects |
| Minimal probability of scarring (depending on the degree of neglect of the pathology) | High price |
| Rapid tissue healing | |
| High efficiency of the method | |
| Minimal damage to healthy tissue | |
| Speed of the procedure |
Wart removal is carried out under local anesthesia. A crust remains at the site of cauterization, which disappears within 14 days. After the procedure, the patient quickly returns to his normal lifestyle, provided that all the doctor's recommendations are followed.
Treatment of filamentous papillomas
In 90% of cases, filarial warts do not heal on their own (like, for example, juvenile or vulgar warts in childhood can heal on their own).
They need to be treated. Especially when these formations are injured.
For example, if the papilloma is on the neck, it can be injured by a chain or clothing collar. If on the face – through glasses, under the breasts – through a bra. You should be aware that such permanent damage can lead to inflammation of this formation and its pain.
Official methods and treatment methods
Removing thread warts with a laser - read a detailed article about laser removal.
The easiest and fastest, and at the same time most affordable, way to treat this type of papillomas. The doctor directs the laser beam at the skin formation, causing it to vaporize and burn out. You should first anesthetize the skin with novocaine so that the patient does not feel any pain. And wear protective glasses for your eyes.
The entire procedure takes no longer than 1 minute per wart. The result is a small crust on the wound. After 3-5 days, this crust comes off and healthy and clean skin forms in this place.
Removal using the radio wave method – read the article about radio wave surgery.
The principle of operation is as follows: a device for radio wave surgery ("Surgitron") generates a high-frequency radio wave that destroys wart tissue in the same way as a laser, i. e. vaporizes it.
The entire procedure is carried out in the same order as with the laser treatment method - first (required! ) local anesthesia, then 1 – 2 minutes of exposure (it all depends on the size of the formation to be removed). The consequences of radio wave treatment are exactly the same as those of laser treatment.
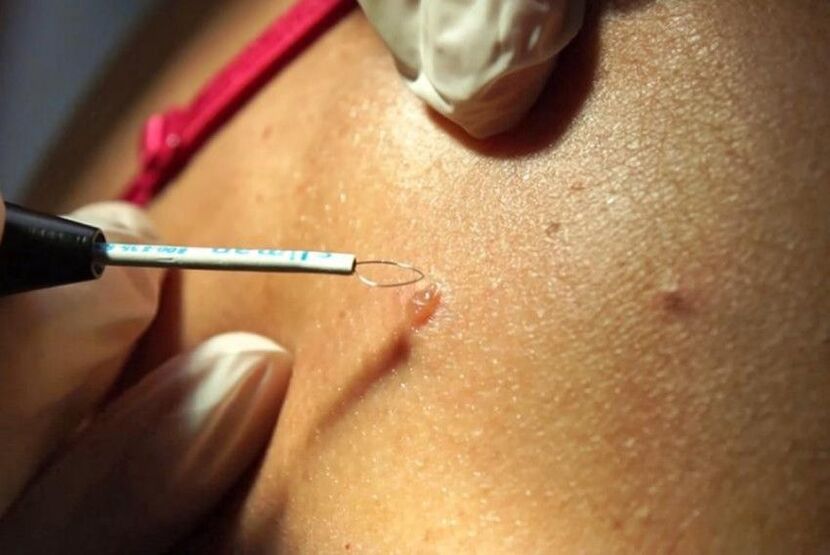
Removal of filamentous papillomas with liquid nitrogen – read information about liquid nitrogen.
This method is popular due to its simplicity. It is not necessary to anesthetize the skin through injections, nor is the presence of a doctor required. The procedure can be performed by any nurse or employee of a cosmetic clinic.
How it works: Liquid nitrogen at a temperature of minus 195 degrees freezes the wart tissue. By timing the effect on the skin, a doctor or nurse prevents the occurrence of frostbite in adjacent healthy skin areas around the pathological formation.
After the procedure is completed, papillomas disappear on their own within 3-4 days in 90% of cases.
Electrocoagulation of thread warts.
Today this method is used much less often as it is a more traumatic method. The papillomas are cut out with an electric knife. This creates a burn and wound on the skin, which then takes longer to heal.
Distance with a radio knife
The most effective modern method of wart removal is removal using radio waves. On the one hand, this is because the instruments in this procedure do not touch the patient's body: they are generated using a radio wave frequency.
Other benefits of radio wave wart removal include:
- complete lack of pain;
- speed of the procedure;
- exclusion of edema and infiltration;
- absence of postoperative complications;
- absence of scars at the wart removal site;
- quick rehabilitation phase.
The procedure is also carried out under local anesthesia. After exposure, a crust forms on the affected skin area, which disappears on its own within 7-10 days.
Prevention of skin tumors
Unfortunately, medicine has not yet learned how to prevent the appearance of various formations on the skin. But dermatologists give their patients the following preventative recommendations:
- Do not hesitate to see a doctor if a tumor appears on the skin.
- Remove formations only after a specialist and diagnosis confirm their benignity.
- Avoid excessive sun exposure.
- Use sunscreen, especially if you are prone to moles and hyperpigmentation.
- do not come into contact with chemically active and carcinogenic substances;
- Do not eat foods that contribute to the development of cancer (smoked meats, sausages, animal fats, meat products with food stabilizers).

























